Outsourcing has become a rising industry in today’s business landscape, allowing businesses to focus on their core competencies while delegating non-essential tasks to specialized providers.
There are various types of outsourcing, each catering to different business needs and requirements. In this article, we will delve into the forms of outsourcing and explore how they can benefit businesses of all sizes.
A Look at Business Process Outsourcing
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) refers to the delegation of non-core operations to third-party service providers. This type of outsourcing covers a wide range of activities, from customer service and human resources to accounting and finance. According to a report by Statista, the global market size of BPO was valued at $25.9 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $43.6 billion by 2025.
Examples of Business Process Outsourcing in Action
To better understand the impact of BPO on businesses, here are some examples of its successful implementation:
- Teleperformance is a leading BPO provider that helped a financial services company improve the customer service and reduce costs by outsourcing its call center operations.
- Wipro is a multinational IT consulting firm providing end-to-end HR outsourcing services to a global technology company, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
- Accenture is a management consulting and professional services company that facilitated services to a multinational consumer goods corporation to streamline its finance and accounting processes that improved accuracy and compliance.
Understanding Professional Outsourcing
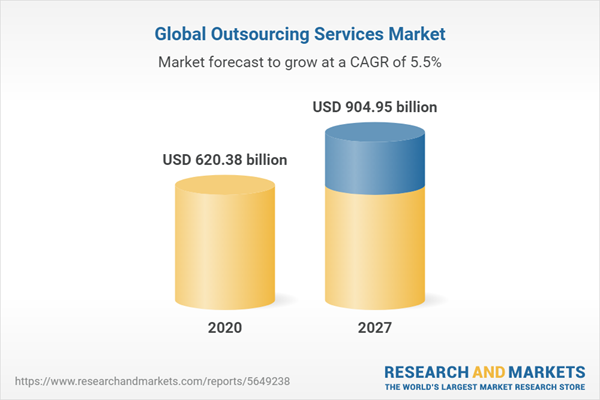
Professional outsourcing refers to hiring specialized professionals to perform specific tasks or projects. This type of outsourcing is used by businesses that require highly skilled expertise that they do not possess in-house. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global professional services outsourcing market is expected to reach $904.95 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.5%.
Mechanics of Professional Outsourcing
Here are some of the benefits of professional outsourcing:
- Access to specialized expertise: Professional outsourcing provides businesses with access to specialized expertise that they may not have in-house.
- Cost savings: Outsourcing specialized tasks or projects can be more cost-effective than hiring full-time employees with the required skill set.
- Improved efficiency: Professional outsourcing allows businesses to focus on their core competencies while delegating specialized tasks to experts, resulting in improved efficiency.
Examples of Professional Outsourcing
Here are some examples of successful implementation of professional outsourcing:
- Uber, a ride-sharing company, outsourced its mapping and navigation tasks to specialized mapping companies to improve the accuracy of its services.
- McDonald’s, a multinational fast-food chain, outsourced its digital transformation to a specialized team to enhance its online ordering system and improve customer experience.
- Google, a multinational technology company, outsourced its language translation services to a team of professional translators to improve the accuracy and efficiency of its translation tools.

IT Outsourcing: A Vital Component of Modern Business
IT outsourcing refers to delegating IT-related tasks and operations to third-party service providers. This type of outsourcing covers a wide range of activities, from software development and network management to cybersecurity and cloud computing. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global IT outsourcing market size was valued at $333.7 billion in 2020 and expected to reach $397.6 billion by 2027.
Examples of IT Outsourcing in Today’s World
- IBM – IBM is a multinational technology company providing IT outsourcing services to a global financial services company that reduced operational costs and improved efficiency.
- Infosys – This is a global IT consulting firm helping a healthcare company improve its digital infrastructure and security by outsourcing its IT operations.
- Tata Consultancy Services – This is an Indian multinational IT services firm giving IT outsourcing services to a global automotive company, which led to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
The Advantages of Multisourcing
Multisourcing refers to the outsourcing to multiple service providers rather than a single provider. Here are some benefits of multisourcing:
- Increased flexibility: Multisourcing allows businesses to adjust their outsourcing strategy as their needs change, providing greater flexibility and agility.
- Access to specialized expertise: Multisourcing allows businesses to access specialized expertise from a range of service providers, enabling them to tackle complex projects or tasks.
- Reduced risk: Multisourcing can help mitigate the risks associated with relying on a single provider, providing greater stability and resilience.
Manufacturing Outsourcing: Benefits and Risks
Manufacturing outsourcing involves the delegation of manufacturing-related tasks to third-party service providers. This type of outsourcing can provide businesses with access to specialized manufacturing capabilities and cost savings, but it also carries risks such as quality control issues and supply chain disruptions. Here are some benefits and risks of manufacturing outsourcing:
Benefits:
- Cost savings: Manufacturing outsourcing can provide businesses with access to cost-effective manufacturing capabilities, resulting in reduced operational costs.
- Access to specialized expertise: Manufacturing outsourcing can provide businesses with access to specialized manufacturing expertise and capabilities that they may not have in-house.
- Increased efficiency: Manufacturing outsourcing can enable businesses to focus on their core competencies while delegating manufacturing-related tasks to specialized providers, resulting in improved efficiency.
Risks:
- Quality control issues: Manufacturing outsourcing can result in quality control issues if the service provider fails to meet the required standards.
- Supply chain disruptions: It can also result in supply chain disruptions if the service provider experiences delays or disruptions in their supply chain.
- Intellectual property risks: Intellectual property is also at risk if the service provider gains access to sensitive information or processes.

Examples of Successful Manufacturing Outsourcing
- Nike – Outsourced its manufacturing to factories in Asia to access cost-effective manufacturing capabilities.
- Apple – Outsourced its manufacturing to Foxconn, a Taiwanese electronics manufacturer, to access specialized manufacturing capabilities and cost savings.
- Procter & Gamble – Outsourced its manufacturing to contract manufacturers to improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Unpacking Process-Specific Outsourcing
Process-specific outsourcing involves outsourcing specific business processes or functions to external service providers. This type of outsourcing can help businesses to focus on core competencies and free up internal resources to focus on strategic business initiatives. Some common types of process-specific outsourcing include:
Accounting and Finance Outsourcing
Outsourcing accounting and finance functions such as bookkeeping, payroll processing, and tax preparation can help businesses save time and reduce costs. According to a study by Deloitte, outsourcing accounting functions can result in cost savings of up to 40%.
Human Resources Outsourcing
Human resources outsourcing involves contracting out HR functions such as recruitment, benefits administration, and employee training and development to external service providers. This type of outsourcing can help businesses to streamline HR processes and reduce administrative burdens.
Customer Service Outsourcing
Outsourcing customer service functions such as call center operations and technical support can help businesses to provide better customer experiences while reducing costs. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global customer service outsourcing market size is expected to reach USD 110.4 billion by 2027.
All About Project Outsourcing
Project outsourcing involves outsourcing specific projects or initiatives to external service providers. This type of outsourcing can help businesses to gain access to specialized expertise, reduce costs, and speed up project completion times.
There are various examples of projects that companies may choose to outsource to external service providers.
- Software development – This is where a company may hire a third-party developer to create custom software that meets its specific needs. This allows the company to focus on its core competencies while leveraging specialized expertise to create a high-quality software product.
- Marketing campaigns – A company hires an advertising agency or marketing firm to handle its advertising, public relations, or social media campaigns. This allows the company to benefit from the marketing expertise of the external agency while freeing up its internal resources for other activities.
- Customer service – Companies may outsource customer support to external service providers who specialize in handling customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests. This can help the company to reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction by providing a more efficient and effective customer support experience.
- Website development, graphic design, content creation, data entry, and administrative tasks such as bookkeeping or payroll management. The decision to outsource a project should be based on a careful evaluation of the risks and benefits, taking into account factors such as cost, quality, expertise, and the impact on the company’s core business activities.
Exploring Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing involves contracting out business processes or functions to service providers located in different countries. Offshore outsourcing can help businesses access specialized skills and reduce costs. Some common examples of offshore outsourcing include:
- Call center services – In this type, companies hire external providers in countries such as India or the Philippines to handle customer service inquiries or technical support.
- Software development – Companies may outsource the development of new software applications or IT infrastructure to teams located in countries such as Ukraine or Russia.
- Manufacturing – It is another area where offshore outsourcing is commonly used, with many companies outsourcing the production of goods to countries such as China, Vietnam, or Mexico to take advantage of lower labor costs. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global contract manufacturing market size is expected to reach USD 118.3 billion by 2026
Examining the Differences between Onshoring and Nearshoring
Onshoring is the practice of outsourcing business processes to companies within the same country as the outsourcing firm. Nearshoring, on the other hand, is the practice of outsourcing business processes to companies in nearby countries. The primary difference between onshoring and nearshoring is the location of the outsourcing firm.
One of the main reasons why companies choose to onshore their operations is to support the local economy. By outsourcing to companies within the same country, businesses can create job opportunities for locals and contribute to the growth of the economy. Additionally, onshoring can help companies reduce costs associated with logistics, communication, and cultural differences that may arise when outsourcing to other countries.
Nearshoring, on the other hand, is preferred by companies that want to take advantage of lower labor costs while still maintaining close proximity to their outsourcing partners. This proximity can help companies reduce communication costs and travel expenses associated with managing offshore outsourcing operations.
Another significant advantage of nearshoring is the ability to leverage similar time zones and cultural similarities. This can help facilitate more effective communication and collaboration between the outsourcing firm and its partners, leading to better project outcomes.

Key Differences of Onshoring and Nearshoring
So, which one is better? It depends on your business needs. If you’re looking to support the local economy and reduce cultural differences and logistics costs, onshoring may be the better option for you. However, if you’re looking to reduce labor costs while still maintaining proximity to your outsourcing partner, nearshoring may be the better choice.
To help you make a more informed decision, here are some key differences between onshoring and nearshoring:
- Labor Costs: While onshoring can help support the local economy, labor costs may be higher due to the higher wages paid to local workers. Nearshoring, on the other hand, can help companies take advantage of lower labor costs in nearby countries.
- Logistics: Onshoring eliminates logistics issues that may arise from outsourcing to other countries, such as time zone differences and language barriers. Nearshoring, on the other hand, can help reduce logistics costs associated with managing offshore outsourcing operations.
- Cultural Differences: Onshoring eliminates cultural differences that may arise when outsourcing to other countries. Nearshoring, on the other hand, may still require companies to navigate some cultural differences, although they may be less significant than those associated with offshore outsourcing.
- Proximity: Onshoring may be preferred by companies that want to maintain close proximity to their outsourcing partners. Nearshoring can also provide proximity benefits, while still allowing companies to take advantage of lower labor costs.
- Time Zones: Onshoring can eliminate time zone differences that may impact project timelines and communication. Nearshoring can also provide similar time zone benefits, while still allowing companies to take advantage of lower labor costs.
In conclusion, onshoring and nearshoring are two viable outsourcing strategies that companies can use to achieve their business goals. When deciding which one to choose, it’s important to consider your business needs, labor costs, logistics, cultural differences, proximity, and time zones. By taking these factors into account, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your business objectives.




